Five solutions to laser welding defects – industrial applications
With the development of industrial manufacturing in the direction of high-end, intelligent and green, driven by the demand of new energy vehicles, lithium batteries, semiconductors and emerging markets, the demand for laser welding has been continuously stimulated, and the application scope and market have been expanding. Especially in the fields of consumer electronics and new energy vehicles, the requirements for laser welding are getting higher and higher, providing a huge market space for laser welding.
However, if any processing method does not master its principle and process, it will produce certain defects or defective products, and laser welding is no exception. Only a good understanding of these defects, and learn how to avoid these defects, in order to better play the value of laser welding, processing a beautiful appearance, good quality products. Chuangxin welding application engineers through long-term experience accumulation, summed up some common welding defects of the solution, for the industry colleagues reference exchange!
01 Crack
The cracks produced in laser continuous welding are mainly hot cracks, such as crystallization cracks, liquefaction cracks, etc., the main reason is that the weld produces a large shrinkage force before the complete solidification, and the measures such as wire filling and preheating can reduce or eliminate the cracks.
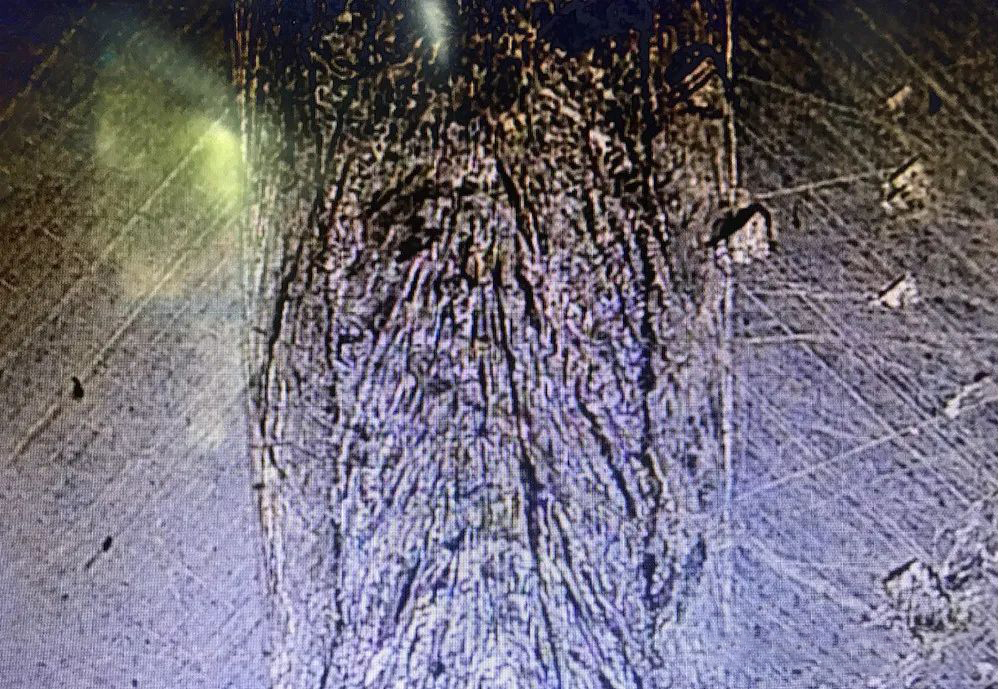
▲ Crack weld
02 Pore
Porosity is one of the most common defects in laser welding. The welding pool of laser welding is deep and narrow, and the cooling speed is fast, and the gas generated in the liquid welding pool does not have enough time to escape, which easily leads to the formation of pores. However, laser welding cools quickly, and the porosity generated is generally smaller than that of traditional fusion welding. Cleaning the surface of the workpiece before welding can reduce the tendency of pores, and the direction of blowing will also affect the formation of pores.
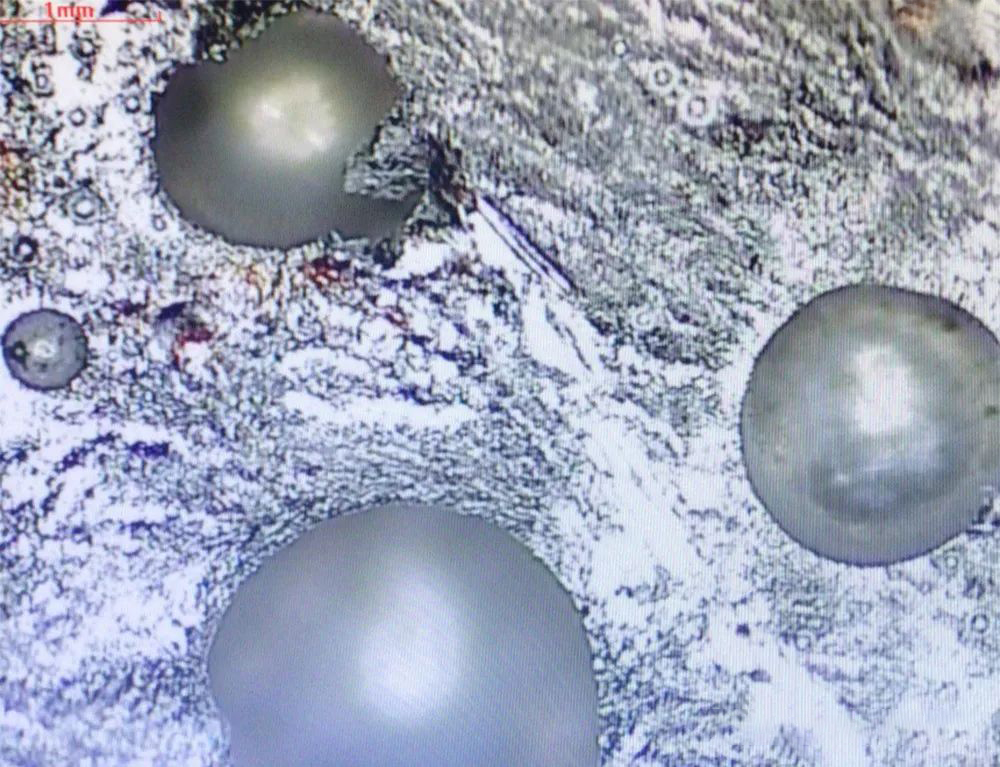
▲ Weld porosity
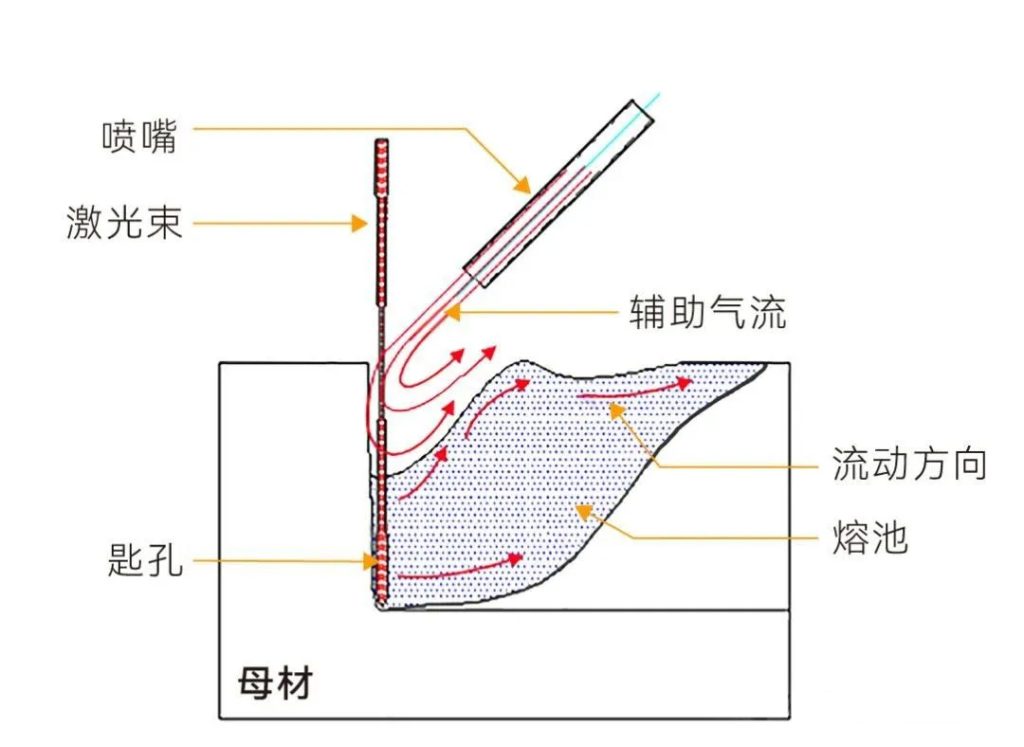
▲ Weld formation process
03 Splash
The splash produced by laser welding seriously affects the weld surface quality and can contaminate and damage the lens. Spatter is directly related to power density, and appropriate reduction of welding energy can reduce spatter. If the penetration is insufficient, the welding speed can be reduced.
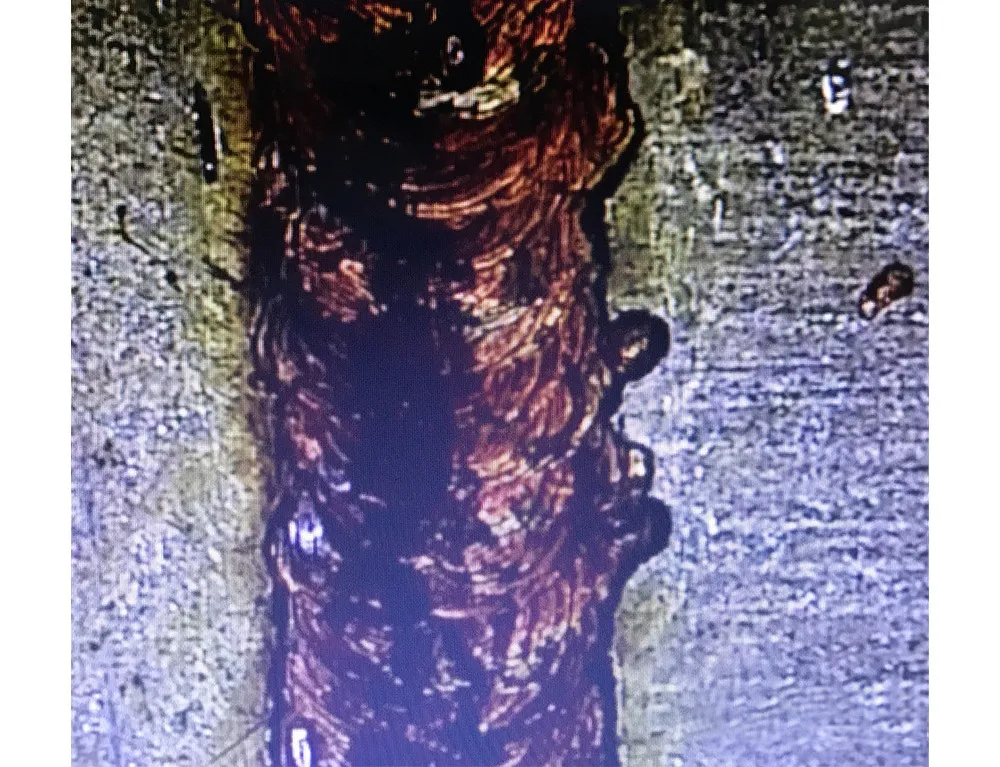
▲ Welding splash
04 Edge bite
If the welding speed is too fast, the liquid metal behind the hole pointing to the center of the weld has no time to redistribute, and the solidification on both sides of the weld will form a bite edge. The joint assembly gap is too large, the melting metal of the caulk is reduced, and the edge is easy to be bitten. At the end of laser welding, if the energy decline time is too fast, the small hole is easy to collapse, resulting in local biting, control power and speed matching can be a good solution to the generation of biting.
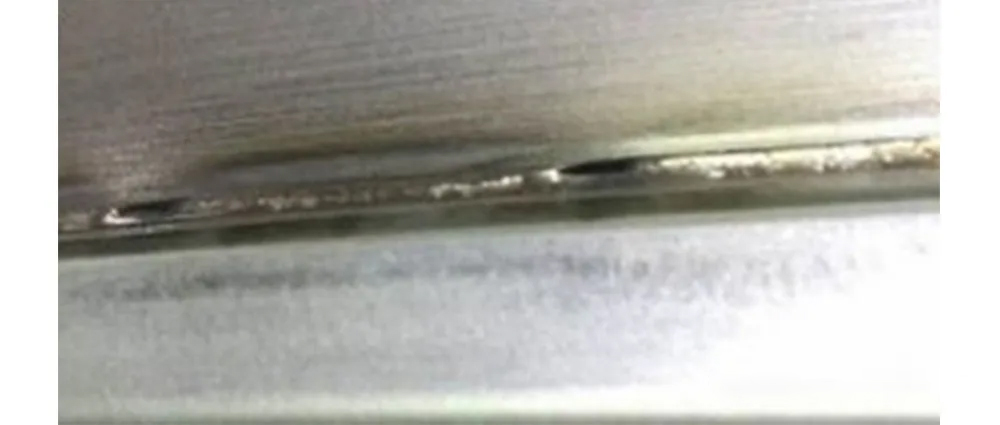

05 Slump
If the welding speed is slow, the molten pool is large and wide, the amount of molten metal increases, and the surface tension is difficult to maintain the heavy liquid metal, the weld center will sink, forming collapse and pits. At this time, it is necessary to properly reduce the energy density to avoid the collapse of the molten pool.
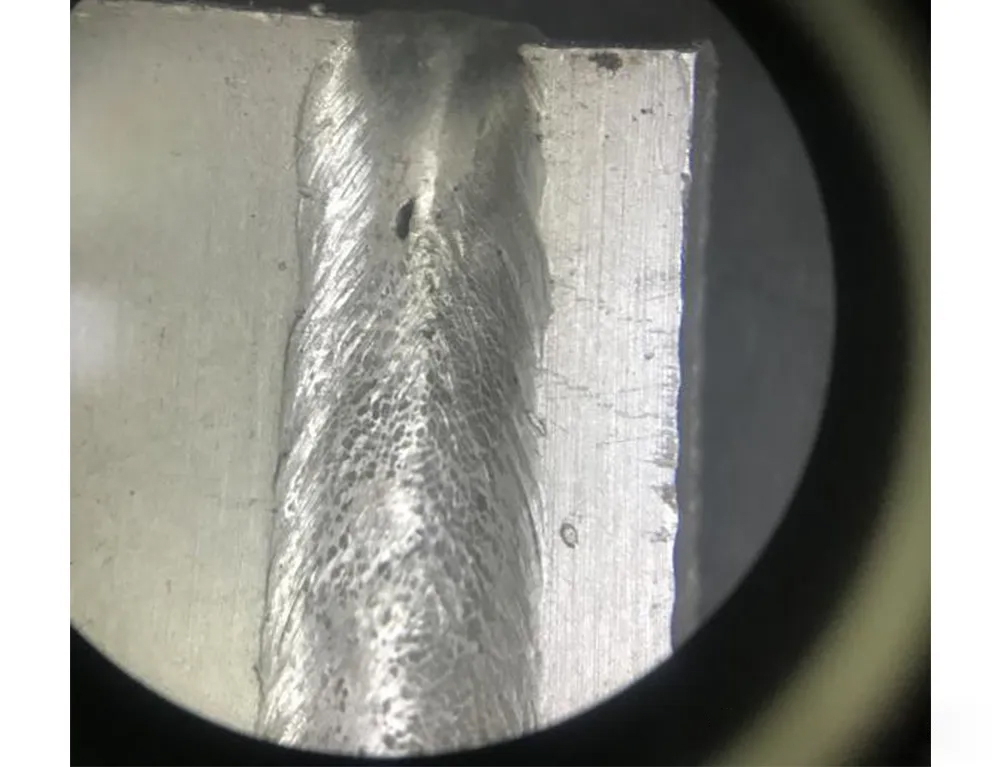

▲ Aluminum alloy weld collapsed
Correctly understand the defects generated in the laser welding process and understand the causes of different defects, you can be more targeted to solve the welding seam anomaly problem in the laser welding process.








